

Bohr's equation and variants of it and the Planck constant invariant equation (Eq.

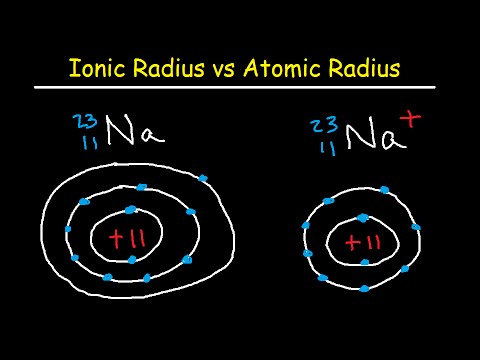
The theoretical research with calculations, showed that the opposing theories are criticised because, they are obsessed with mathematical complexities with ambiguities without common ground that should usher alternative solution to the problem of the size of atom and thus, they cannot be considered as a valid description of reality. The research was undertaken with the following objectives: 1) to review concerns about atomism 2) appraise the issues of mathematical complexities in HUP and SE 3) review criticism against SE and HUP 4) most importantly derive a Planck constant invariant equation for the calculation of any atomic radii and 5) recalculate the radii of selected elements chosen for their biological importance. A simple method of computing the absolute size of atoms has been explored and a large body of known material has been brought together to reveal how many different properties correlate with atomic size.Ĭoncern has been expressed against the new theories, Heisenberg uncertainty principle (HUP) and Schrödinger wave/quantum mechanics (SE) that are purported to have replaced Bohr's theory and equation. The calculated global hardness and atomic polarizability of a number of atoms are found to be close to the available experimental values and the profiles of the physical properties computed in terms of the theoretical atomic radii exhibit their inherent periodicity. The radii are used to calculate a number of size dependent periodic physical properties of isolated atoms viz., the diamagnetic part of the atomic susceptibility, atomic polarizability and the chemical hardness. The computed sizes qualitatively correlate with the absolute size dependent properties like ionization potentials and electronegativity of elements. The d-block and f-block contractions are distinct in the calculated sizes. The set of theoretical radii are found to reproduce the periodic law and the Lother Meyer’s atomic volume curve and reproduce the expected vertical and horizontal trend of variation in atomic size in the periodic table. A set of theoretical atomic radii corresponding to the principal maximum in the radial distribution function, 4Àr2R2 for the outermost orbital has been calculated for the ground state of 103 elements of the periodic table using Slater orbitals. A New One-Pot Sequential Reduction-Deposition Method for the synthesis of Silica-supported NiPt and CuPt Bimetallic Catalysts. Tyrone Ghampson, Gwang-Nam Yun, Yasukazu Kobayashi, Atsushi Takagaki, S.
Journal of the American Chemical Society 2003, 125 Mechanism for the Cyclotrimerization of Alkynes and Related Reactions Catalyzed by CpRuCl. Karl Kirchner, Maria José Calhorda, Roland Schmid, and, Luís F.
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2018, 122 Real-Time Tracking of Polymer Crystallization Dynamics in Organic Bulk Heterojunctions by Raman Microscopy. Hands-On Experiment To Verify Consistency from Bulk Density to Atomic and Ionic Radii with Lumps of Metals and Ionic Compounds.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
